(By Khalid Masood)
In the rapidly evolving landscape of military technology, autonomous military robots have become essential for enhancing operational efficiency while minimizing risks to human soldiers. These advanced machines carry out a diverse range of tasks—from reconnaissance to explosive ordnance disposal—with remarkable precision and reliability. By integrating artificial intelligence, advanced sensors, and enhanced mobility, they can navigate complex battlefields independently, adapting to challenging environments with minimal human intervention. As we examine the top 10 autonomous military robots in 2025, it is clear that these innovations are reshaping modern warfare through intelligent decision-making and robust adaptability across varied terrains worldwide. Many leverage AI for real-time pathfinding and tactical decisions, while countries prioritize durability and flexibility to operate in diverse conditions. Despite these advances, limitations such as battery life and lingering ethical questions continue to challenge wider adoption.
This review focuses on the globally deployed military robots that define the forefront of defense robotics, detailing each system’s history, specifications, primary operators, and operational strengths and weaknesses. Additionally, it addresses common inquiries such as “What are the best autonomous military robots in 2025?” and “Which countries lead in deploying advanced defense robotics?” Drawing from defense analyses and expert sources, this article delivers comprehensive insights to help readers understand these game-changing technologies.
Autonomous military robots typically rely on sophisticated AI algorithms to enable independent navigation and task execution, reducing frontline soldier exposure in high-risk combat zones. Equipped with sensors such as LIDAR and high-resolution cameras, they process real-time data essential for battlefield awareness. Estimates suggest there are over 10,000 such robots deployed worldwide, with the United States leading in numbers. Israel excels in developing models tailored for urban combat, while Estonia innovates with versatile ground vehicles. Meanwhile, Russia and China continue investing heavily to produce advanced platforms optimized for asymmetric warfare.
1. PackBot: Pioneering the Top 10 Autonomous Military Robots of the World
The PackBot originated in the late 1990s from iRobot’s research of USA into portable robotics. It designed for urban search and rescue initially. PackBot was adapted post-9/11 for explosive ordnance disposal (EOD). Its first major combat deployment was in Afghanistan in 2002, and it quickly became indispensable in Iraq’s IED-ridden battlefields.
Weighing 18 kg with tracked mobility, PackBot achieves speeds up to 9.3 km/h and can manipulate up to 20 kg with its robotic arms. Its AI-enabled autonomous waypoint navigation allows semi-autonomous patrols in dangerous environments, while integrated sensors detect chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear threats. Powered by lithium-ion batteries lasting roughly four hours, its ability to climb stairs and resist water up to one meter adds to its versatility.
PackBot serves in over 20 countries including the U.S., UK, Australia, Israel, and France. Despite newer platforms emerging, this robot remains crucial across NATO and allied missions due to its reliability, cost-efficiency, and battlefield-proven durability. Limitations include battery constraints, vulnerability during remote control interruptions, and payload restrictions.

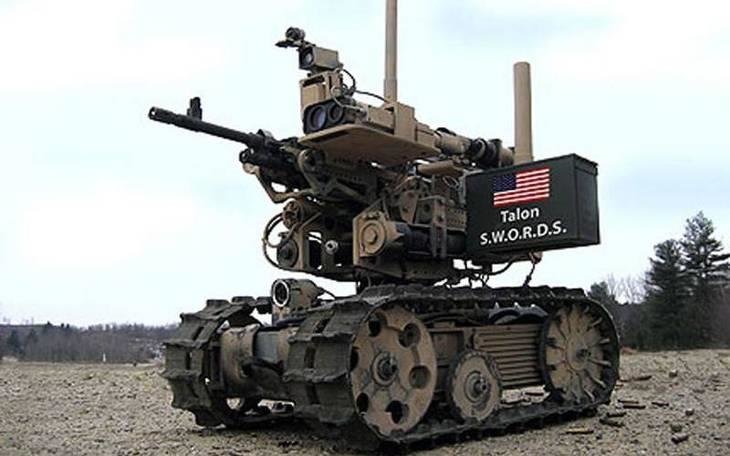
2. TALON: Versatile in the Top 10 Autonomous Military Robots of the World
The TALON robot developed in the early 2000s by QinetiQ for EOD tasks. It aimed to replace human risk in bomb disposal. It was later acquired by FLIR Systems, TALON debuted in 2000 and has since supported explosive disposal operations worldwide, including Bosnia, Afghanistan, Iraq, and Syria. With a robust frame weighing 52 kg, it features 45 kg manipulator arms, thermal cameras, and chemical sensors.
Its battery supports up to seven hours of operation at speeds reaching 8 km/h. TALON’s tracked mobility enables stair climbing and operation in harsh environments. Over 40 countries maintain TALON units, capitalizing on its stealthy, low-noise profile and high endurance.
Though its limited remote control range and heavy weight affect portability, TALON remains a premier EOD asset, constantly enhanced to expand its semi-autonomous capabilities.

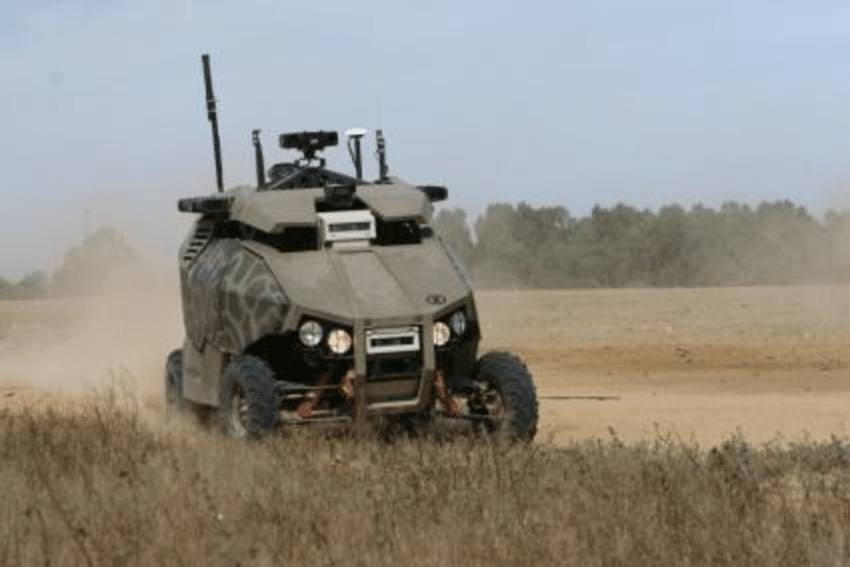
3. Guardium: Border Sentinel in the Top 10 Autonomous Military Robots of the World
Guardium, developed by G-NIUS for the Israel Defense Forces, was fielded in 2009 to secure volatile borders such as Gaza and Lebanon. Powered by a diesel engine providing 24-hour autonomy, the wheeled Guardium travels up to 50 km/h and can patrol autonomously up to 50 km radius using GPS and AI obstacle avoidance.
Its modular payload includes sophisticated cameras and armed variants equipped with machine guns for rapid response. Besides Israel, Guardium aids border security in Azerbaijan and Singapore.
While offering continuous surveillance and intrusion detection, its wheeled design faces rough terrain limitations, and vulnerability to IEDs remains a concern. Nevertheless, Guardium exemplifies successful long-endurance robotic border security.

4. MQ-9 Reaper: Aerial Power in the Top 10 Autonomous Military Robots of the World
The MQ-9 Reaper developed in the 2000s by General Atomics for US Air Force. It aimed for armed reconnaissance. Moreover, the first flight occurred in 2001. The robot entered service in 2007. The MQ-9 Reaper drone exemplifies airborne autonomous platforms with strike capabilities. First flown in 2001 and operational from 2007, it flies at speeds near 482 km/h with endurance up to 27 hours and a 1,850 km range.
Outfitted with an array of sensors including infrared cameras and AESA radar, its lethal payloads encompass Hellfire missiles and laser-guided bombs. AI enables semi-autonomous flight, including auto takeoff and landing.
Used by over 15 nations, including the U.S., UK, Italy, France, and India (planning acquisition), the Reaper has made a profound impact in theaters such as Afghanistan, Iraq, Libya, and Yemen. Ethical controversies over collateral damage and electronic warfare vulnerabilities remain challenges.

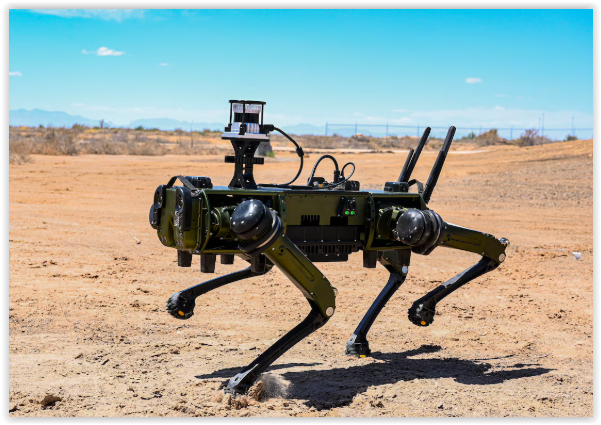
5. Ghost Robotics Vision 60: Quadruped in the Top 10 Autonomous Military Robots of the World
The Ghost Robotics Vision 60 developed in the 2010s for rugged terrain navigation. It aimed for military scouting. Vision 60 is a landmark legged robot built to operate on complex, uneven terrain by emulating animal movement. Its agility surpasses wheeled or tracked alternatives, excelling in reconnaissance and urban combat support.
Deployed since 2020 and tested extensively by the U.S. Air Force and NATO partners, Vision 60 carries advanced sensors for mapping and threat detection, supported by AI that enables autonomous navigation and obstacle avoidance. Its 10 km/h top speed and 3-hour battery life afford flexible mission profiles.
Though limited by battery endurance and potential physical damage to its legs, Vision 60 forecasts a growing shift toward legged locomotion in military robotics.

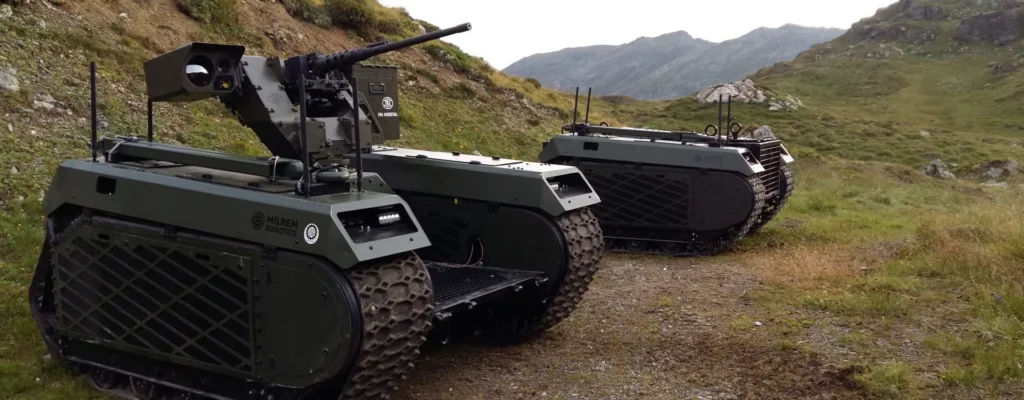
6. Milrem THeMIS: Ground Vehicle in the Top 10 Autonomous Military Robots of the World
The Milrem THeMIS developed in the 2010s by Estonia for logistics. It aimed for unmanned support in combat. Estonia’s Milrem THeMIS is a modular unmanned ground vehicle that still supports logistics, casualty evacuation, and combat roles globally. It features a tracked platform combining diesel and electric propulsion for up to 20 km/h speeds, carrying payloads up to 750 kg.
Operational since 2018 in Mali and Ukraine, THeMIS incorporates AI-based pathfinding to independently navigate difficult terrains. Its modularity enables adaptation for medical, supply, and armed roles, significantly alleviating soldier workload.
While battery limitations and slower road speeds are drawbacks, its multifunctionality marks a new era in autonomous support vehicles.

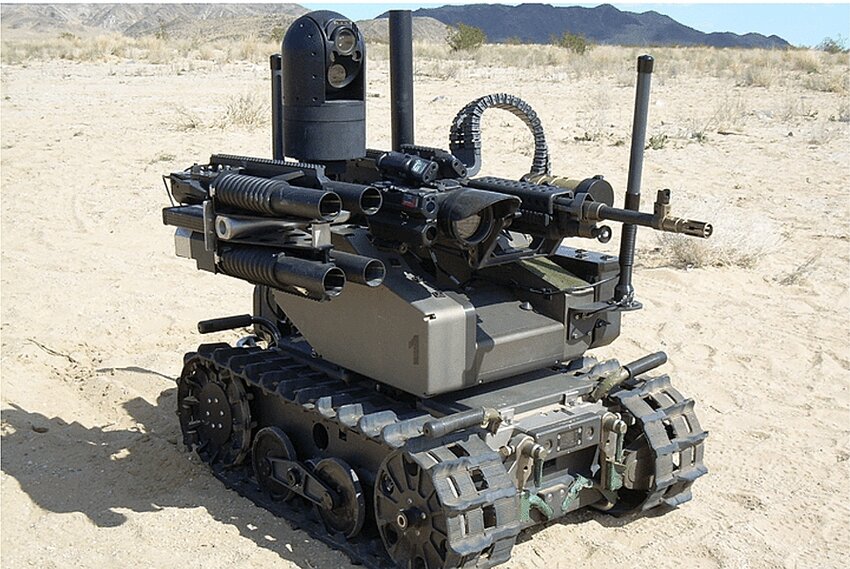
8. QinetiQ MAARS: Modular in the Top 10 Autonomous Military Robots of the World
The QinetiQ MAARS developed in the 2000s for armed reconnaissance. It aimed for remote combat. It has been in development and testing since 2008, offering remote-controlled firepower with machine guns and grenade launchers mounted on a wheeled chassis.
MAARS combines target detection cameras with AI sentry mode for autonomous engagement in defended perimeters. Its lightweight frame (112 kg) enhances transportability in urban environments.
Though deployment remains limited primarily to training and trials due to ethical and EMP concerns, MAARS paves the way for remotely operated lethal robots.

9. Samsung SGR-A1: Sentry in the Top 10 Autonomous Military Robots of the World
The Samsung SGR-A1 developed in the 2000s for border guard. South Korea needed automated surveillance. The Samsung SGR-A1 was deployed along the Korean Demilitarized Zone starting in 2006, providing automated surveillance with AI-enabled human target recognition and lethally armed turrets.
Though fixed in position, the system offers 24/7 vigilance with low operating costs. Ethical armament restrictions limit autonomous firing modes, balancing automation with human judgment.
SGR-A1 remains the only deployed armed border robot of its kind as of 2025.

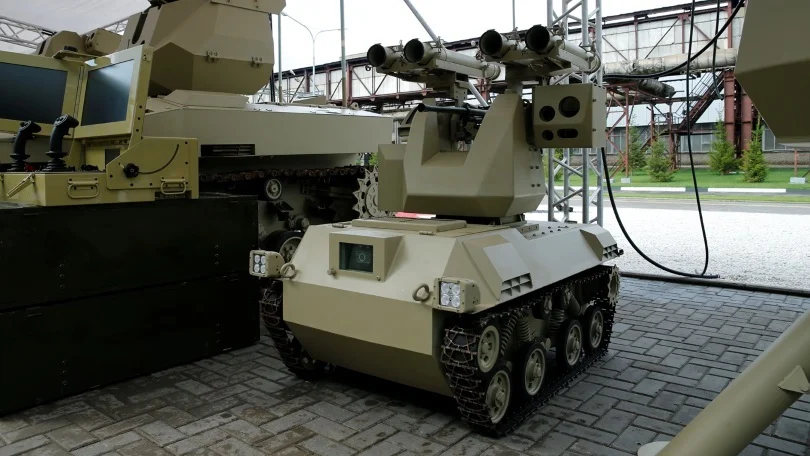
10. Kalashnikov Companion: Russian Companion in the Top 10 Autonomous Military Robots of the World
The Kalashnikov Companion developed in the 2010s for combat support and began production in 2017 and engaged operationally in Syria from 2019 onward, with armed variants participating in the Ukraine conflict since 2022.
Its tracked chassis navigates rough terrain at speeds up to 35 km/h and supports remote operation up to 10 km. Equipped with PK machine guns and reconnaissance cameras, it autonomously follows infantry formations, enhancing soldier protection.
Despite ongoing developmental challenges, Kalashnikov Companion reflects Russia’s commitment to integrated man-machine combat.

Conclusion: The Future of Top 10 Autonomous Military Robots of the World
From the PackBot to Kalashnikov Companion, these top 10 autonomous military robots of the world demonstrate robotics evolution. In 2025, models like Vision 60 lead in mobility, while MQ-9 Reaper excels in aerial tasks. Moreover, robots adapt to AI for autonomy. However, challenges like ethics persist. Therefore, understanding top 10 autonomous military robots of the world reveals trends. As warfare changes, innovations will shape roles. Additionally, global use grows. The future holds swarms and AI teams. This transforms defence. Overall, these robots are vital.