(By Khalid Masood)
In the ever-changing landscape of global security, navies serve as critical instruments for projecting power and protecting interests. These forces maintain maritime dominance through advanced ships, submarines, and aircraft carriers. Moreover, they adapt to modern challenges like territorial disputes and piracy with innovative technologies. As we analyse 2025, the top 10 navies of the world highlight a mix of numerical strength and qualitative superiority. For instance, many emphasise aircraft carriers for extended reach and blue-water operations. Additionally, nations focus on navies that balance budget constraints with operational effectiveness. However, some rely on legacy fleets for immediate readiness. This article explores each navy’s history, fleet details, strengths, and weaknesses, based on military assessments. Furthermore, it answers questions like “what are the strongest navies in 2025?” or “which countries have the largest fleets?” Drawing from defence reports and expert sources, we offer in-depth views. Therefore, readers can appreciate these maritime powerhouses.
Navies typically include surface combatants, submarines, and support vessels for diverse missions. They prioritise tonnage for endurance and firepower in open seas. Additionally, integration with air and land forces enhances effectiveness. According to rankings, the United States leads with superior technology, while China excels in sheer numbers. Meanwhile, Russia maintains a strong submarine focus despite challenges. However, Asian navies like Indonesia and South Korea rise through modernisation. Consequently, the top 10 navies of the world reflect strategic priorities worldwide. Forces in the Indo-Pacific, Atlantic, and Mediterranean deploy them for patrols and exercises. For example, joint operations demonstrate interoperability among allies. Overall, these navies shape international relations. As threats evolve, investments ensure relevance. Thus, this compilation features premier fleets in 2025.
1. United States Navy: Dominating the Top 10 Navies of the World
The United States Navy traces its origins to 1775 during the American Revolution. It formalised in 1794 to combat piracy and protect commerce. Moreover, it expanded during World War II with massive shipbuilding. The navy played key roles in conflicts like Vietnam and Iraq. Additionally, post-Cold War shifts focused on power projection. The fleet grew with nuclear carriers in the 1960s. However, budget cuts in the 1990s reduced size. This led to modernisation efforts. Furthermore, it integrates with allies through NATO. Overall, it remains the world’s premier blue-water force.
Specifications include 440 warships in 2025. The fleet boasts 11 nuclear-powered aircraft carriers. Submarines number 68, with Virginia-class attack models. Moreover, destroyers like Arleigh Burke-class total 73. Frigates are transitioning to Constellation-class. The budget exceeds $240 billion annually. Additionally, tonnage reaches 4.17 million. Aircraft carriers displace 100,000 tonnes each. Submarines feature advanced sonar and missiles. This enables global operations.
Operators are the United States Department of Defense. It deploys worldwide from bases in Virginia and California. Moreover, forward presence in Japan and Bahrain. The navy supports operations in the Pacific and Middle East. Additionally, it aids humanitarian missions. No other countries operate it. However, allies benefit from joint exercises. Overall, it safeguards US interests globally.
Pros feature unmatched carrier strike groups. It projects power across oceans. Moreover, advanced technology like Aegis systems enhances defence. Integration with satellites improves coordination. The large budget allows innovation. Additionally, extensive training ensures readiness. Effectiveness shown in exercises like RIMPAC. Furthermore, nuclear submarines provide stealth. This suits strategic deterrence.
Cons involve high maintenance costs for carriers. Budget constraints limit new builds. Moreover, ageing ships require upgrades. Recruitment challenges affect manning. The fleet vulnerabilities to hypersonics exist. Additionally, overstretch from global commitments. Political debates delay funding. However, reforms address issues. Overall, it demands sustained investment.

2. People’s Liberation Army Navy: Rising in the Top 10 Navies of the World
The People’s Liberation Army Navy began in 1949 after the Chinese Civil War. It started as a riverine force with defected ships. Moreover, Soviet aid in the 1950s built submarines and destroyers. Expansion occurred in the 1970s for coastal defence. Additionally, the 1980s saw blue-water ambitions. The navy modernised post-1990s with carrier programmes. However, territorial disputes accelerated growth. This led to rapid shipbuilding. Furthermore, it now rivals Western fleets. Overall, it symbolises China’s maritime rise.
Specifications show 754 warships in 2025. The fleet includes 3 aircraft carriers like Shandong. Submarines number 60, with Type 093 nuclear models. Moreover, destroyers like Type 055 total 32. Frigates exceed 50 Type 054A. The budget is $200 billion yearly. Additionally, tonnage is 2.85 million. Carriers displace 60,000 tonnes. Submarines feature ballistic missiles. This supports Indo-Pacific operations.
Operators are the People’s Republic of China. It deploys from bases in Hainan and Qingdao. Moreover, outposts in the South China Sea. The navy patrols disputed areas. Additionally, it conducts global voyages. No foreign operators exist. However, alliances with Pakistan share technology. Overall, it asserts regional dominance.
Pros include largest fleet numbers for mass deployments. It counters adversaries with anti-access strategies. Moreover, rapid construction speeds modernisation. Integration with satellites boosts targeting. The budget enables innovation. Additionally, amphibious capabilities aid island claims. Effectiveness in exercises like Vostok. Furthermore, nuclear submarines enhance deterrence. This fits expansion goals.
Cons feature limited carrier experience. Quality issues in early ships persist. Moreover, crew training lags Western standards. Dependence on foreign engines. The fleet vulnerabilities to submarines exist. Additionally, international tensions from assertions. Budget opacity raises concerns. However, reforms improve. Overall, it needs operational maturity.

3. Russian Navy: Enduring Presence in the Top 10 Navies of the World
The Russian Navy originated in 1696 under Peter the Great. It expanded during imperial eras with Baltic fleets. Moreover, Soviet times saw massive submarine builds. The navy peaked in the Cold War with carriers. Additionally, post-1991 dissolution reduced size. The 2000s revival focused on modernisation. However, Ukraine conflicts damaged assets. This prompted repairs. Furthermore, it maintains Arctic presence. Overall, it reflects Russia’s strategic depth.
Specifications include 419 warships in 2025. The fleet has 1 aircraft carrier, Admiral Kuznetsov. Submarines number 55, with Borei-class ballistic. Moreover, destroyers like Sovremenny-class total 10. Frigates are 11 Admiral Gorshkov. The budget is $60 billion annually. Additionally, tonnage is 1.26 million. Carrier displaces 58,000 tonnes. Submarines carry hypersonic missiles. This enables Northern operations.
Operators are the Russian Federation. It deploys from Sevastopol and Vladivostok. Moreover, Mediterranean task forces. The navy supports Syria missions. Additionally, it conducts Arctic patrols. No foreign operators. However, alliances with Syria share bases. Overall, it secures Eurasian waters.
Pros feature strong submarine deterrence. It deploys hypersonic weapons effectively. Moreover, icebreakers aid Arctic navigation. Integration with air forces enhances strikes. The budget allows upgrades. Additionally, expeditionary capabilities in Syria. Effectiveness in Black Sea. Furthermore, nuclear submarines provide stealth. This suits asymmetric warfare.
Cons involve ageing carrier reliability. Sanctions limit parts. Moreover, losses in Ukraine weaken fleet. Crew shortages affect readiness. The fleet vulnerabilities to drones exist. Additionally, short global reach. Budget cuts delay projects. However, innovations continue. Overall, it requires renewal.

4. Indonesian Navy: Regional Leader in the Top 10 Navies of the World
The Indonesian Navy formed in 1945 during independence struggles. It started with captured Japanese ships. Moreover, Dutch colonial legacies shaped early fleets. Expansion happened in the 1960s with Soviet aid. Additionally, the 1990s saw modernisation for archipelago defence. The navy responded to tsunamis and piracy. However, budget limits constrained growth. This led to international partnerships. Furthermore, it focuses on maritime sovereignty. Overall, it guards vast islands.
Specifications show 331 warships in 2025. The fleet includes 0 carriers but helicopter platforms. Submarines number 4 Nagapasa-class. Moreover, frigates like Martadinata-class total 7. Corvettes are 25 Diponegoro-class. The budget is $2 billion yearly. Additionally, tonnage is 330,200. Submarines displace 1,400 tonnes. Frigates carry anti-ship missiles. This supports coastal patrols.
Operators are the Republic of Indonesia. It deploys from Surabaya and Jakarta. Moreover, bases in the Malacca Strait. The navy combats smuggling. Additionally, it participates in ASEAN exercises. No foreign operators. However, collaborations with Australia share intelligence. Overall, it secures sea lanes.
Pros include large patrol fleet for archipelagos. It counters piracy effectively. Moreover, affordable vessels suit budgets. Integration with coast guards enhances. The numbers provide coverage. Additionally, humanitarian roles in disasters. Effectiveness in exercises. Furthermore, submarine growth adds depth. This fits regional needs.
Cons involve no carriers for power projection. Technology lags advanced navies. Moreover, maintenance issues with old ships. Crew training varies. The fleet vulnerabilities to submarines exist. Additionally, vast area strains resources. Budget constraints limit upgrades. However, partnerships help. Overall, it needs investment.

5. Republic of Korea Navy: Technological Force in the Top 10 Navies of the World
The Republic of Korea Navy established in 1945 after liberation. It began with small patrol boats. Moreover, US aid in the 1950s built destroyers. Expansion occurred during the Cold War for North threats. Additionally, the 1990s saw indigenous shipbuilding. The navy expanded for blue-water roles. However, tensions with North Korea shaped focus. This led to submarine emphasis. Furthermore, it joins US alliances. Overall, it protects peninsula seas.
Specifications include 227 warships in 2025. The fleet has 1 helicopter carrier, Dokdo-class. Submarines number 20, with Dosan Ahn Changho-class. Moreover, destroyers like Sejong the Great total 12. Frigates are 9 Incheon-class. The budget is $5 billion annually. Additionally, tonnage is 500,000. Carrier displaces 18,800 tonnes. Submarines carry ballistic missiles. This enables regional deterrence.
Operators are the Republic of Korea. It deploys from Busan and Jeju. Moreover, joint bases with US. The navy patrols Yellow Sea. Additionally, it conducts anti-submarine drills. No foreign operators. However, alliances with Japan share data. Overall, it counters northern threats.
Pros feature advanced Aegis destroyers. It deploys ballistic submarines effectively. Moreover, domestic building reduces costs. Integration with US enhances. The technology provides edge. Additionally, amphibious capabilities for islands. Effectiveness in exercises. Furthermore, carrier plans add projection. This suits defensive postures.
Cons involve limited carrier experience. Numbers smaller than neighbours. Moreover, crew recruitment challenges. Dependence on US tech. The fleet vulnerabilities to missiles exist. Additionally, short global reach. Budget pressures from army. However, innovations continue. Overall, it requires expansion.

6. Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force: Precision in the Top 10 Navies of the World
The Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force formed in 1954 under the constitution. It started as a coastal defence force. Moreover, US aid provided destroyers. Expansion happened in the 1980s for Soviet threats. Additionally, the 2000s saw helicopter carriers. The force modernised for island disputes. However, pacifist laws limited offensives. This led to defensive focus. Furthermore, it allies with US. Overall, it guards sea lanes.
Specifications show 105 warships in 2025. The fleet includes 2 helicopter carriers, Izumo-class. Submarines number 23, with Taigei-class. Moreover, destroyers like Maya-class total 8. Frigates are 6 Mogami-class. The budget is $7 billion yearly. Additionally, tonnage is 276,166. Carriers displace 27,000 tonnes. Submarines feature lithium batteries. This supports Pacific operations.
Operators are Japan. It deploys from Yokosuka and Sasebo. Moreover, bases in Okinawa. The force patrols Senkaku Islands. Additionally, it joins RIMPAC exercises. No foreign operators. However, alliances with Australia share training. Overall, it secures trade routes.
Pros include high-tech destroyers for anti-missile. It deploys stealth submarines effectively. Moreover, domestic industry innovates. Integration with US boosts. The quality exceeds numbers. Additionally, carrier conversions add air power. Effectiveness in drills. Furthermore, ASW expertise counters threats. This fits alliance roles.
Cons involve no offensive carriers constitutionally. Fleet smaller than rivals. Moreover, ageing ships need replacement. Crew shortages from demographics. The force vulnerabilities to carriers exist. Additionally, limited global deployment. Budget caps by GDP. However, reforms relax rules. Overall, it demands adaptation.

7. Indian Navy: Emerging in the Top 10 Navies of the World
The Indian Navy traces roots to ancient maritime traditions. It formalised in 1612 with East India Company. Moreover, British colonial era built ports. Independence in 1947 created the modern navy. Expansion occurred in the 1960s for Pakistan threats. Additionally, the 1980s saw carrier acquisitions. The navy expanded for Indian Ocean dominance. However, budget limits constrained. This led to indigenous builds. Furthermore, it focuses on blue-water. Overall, it asserts regional power.
Specifications include 293 warships in 2025. The fleet has 2 aircraft carriers, Vikrant-class. Submarines number 17, with Kalvari-class. Moreover, destroyers like Kolkata-class total 10. Frigates are 11 Talwar-class. The budget is $8 billion annually. Additionally, tonnage is 593,603. Carriers displace 45,000 tonnes. Submarines carry cruise missiles. This enables Indo-Pacific patrols.
Operators are the Republic of India. It deploys from Mumbai and Visakhapatnam. Moreover, bases in Andaman Islands. The navy patrols Malacca Strait. Additionally, it conducts anti-piracy missions. No foreign operators. However, alliances with Quad share exercises. Overall, it secures energy routes.
Pros feature indigenous carriers for projection. It deploys nuclear submarines effectively. Moreover, growing fleet counters China. Integration with air force enhances. The diversity provides versatility. Additionally, humanitarian roles in tsunamis. Effectiveness in exercises. Furthermore, missile tech adds strike. This suits expansion.
Cons involve delays in projects. Quality issues in builds. Moreover, submarine shortages. Crew training varies. The fleet vulnerabilities to carriers exist. Additionally, vast area strains. Budget constraints from army. However, reforms accelerate. Overall, it needs speed.

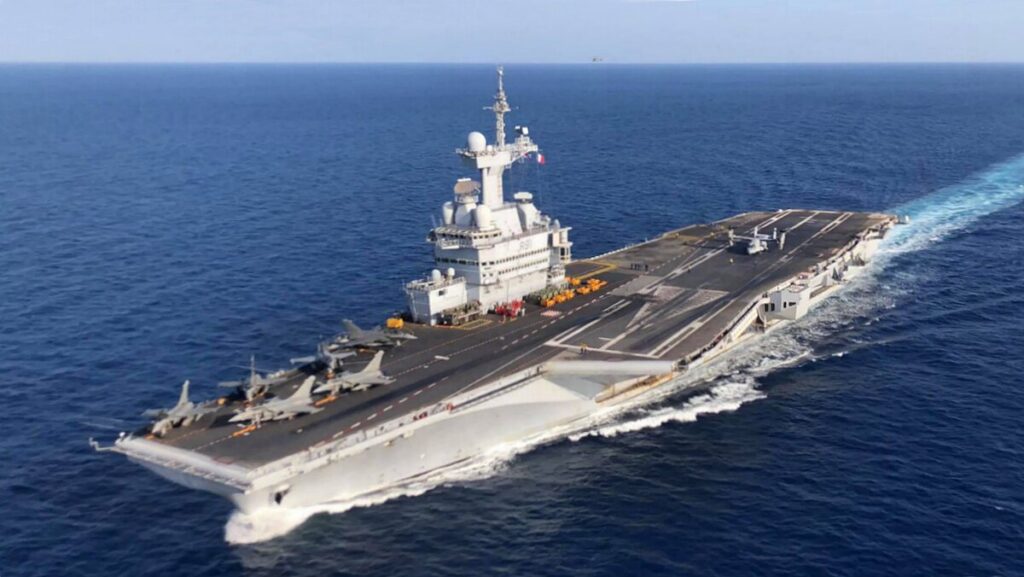
8. French Navy: Versatile in the Top 10 Navies of the World
The French Navy dates to 1624 under Richelieu. It expanded during colonial eras. Moreover, World Wars saw carrier developments. Post-1945, it rebuilt for NATO roles. Additionally, the 1960s nuclear focus. The navy expanded for overseas territories. However, budget cuts reduced size. This led to multinational partnerships. Furthermore, it maintains global presence. Overall, it protects interests.
Specifications include 128 warships in 2025. The fleet has 1 nuclear carrier, Charles de Gaulle. Submarines number 10, with Barracuda-class. Moreover, destroyers like Horizon-class total 2. Frigates are 11 Aquitaine-class. The budget is $6 billion yearly. Additionally, tonnage is 400,000. Carrier displaces 42,000 tonnes. Submarines feature pump-jet propulsion. This supports Atlantic operations.
Operators are the French Republic. It deploys from Toulon and Brest. Moreover, bases in New Caledonia. The navy patrols Mediterranean. Additionally, it joins EU missions. No foreign operators. However, alliances with UK share carriers. Overall, it secures colonies.
Pros include nuclear carrier for strike. It deploys ballistic submarines effectively. Moreover, advanced frigates for anti-air. Integration with EU enhances. The quality provides edge. Additionally, expeditionary capabilities in Africa. Effectiveness in Mali. Furthermore, nuclear tech adds deterrence. This fits overseas roles.
Cons involve small fleet numbers. Ageing submarines need replacement. Moreover, budget limits expansions. Crew shortages affect. The fleet vulnerabilities to submarines exist. Additionally, short global reach. Political debates delay. However, partnerships help. Overall, it requires growth.

9. Royal Navy: Historic Force in the Top 10 Navies of the World
The Royal Navy originated in 1660 under Charles II. It dominated during imperial times with battleships. Moreover, World Wars saw carrier innovations. Post-1945, it adapted for NATO. Additionally, the 1980s Falklands victory. The navy modernised for expeditionary roles. However, cuts reduced size. This led to carrier focus. Furthermore, it allies with US. Overall, it upholds tradition.
Specifications include 117 warships in 2025. The fleet has 2 carriers, Queen Elizabeth-class. Submarines number 10, with Astute-class. Moreover, destroyers like Type 45 total 6. Frigates are 11 Type 23. The budget is $7 billion annually. Additionally, tonnage is 400,000. Carriers displace 65,000 tonnes. Submarines carry Tomahawks. This enables global deployments.
Operators are the United Kingdom. It deploys from Portsmouth and Clyde. Moreover, bases in Gibraltar. The navy patrols North Atlantic. Additionally, it conducts freedom operations. No foreign operators. However, alliances with Five Eyes share intel. Overall, it projects power.
Pros feature advanced carriers for air strikes. It deploys nuclear submarines effectively. Moreover, Type 45 destroyers for anti-missile. Integration with NATO enhances. The training excels. Additionally, amphibious capabilities for landings. Effectiveness in exercises. Furthermore, cyber tech adds. This suits alliances.
Cons involve reduced fleet from cuts. Carrier vulnerabilities to missiles. Moreover, submarine shortages. Recruitment issues persist. The fleet ageing frigates need. Additionally, short numbers strain. Budget debates delay. However, reforms continue. Overall, it demands revival.

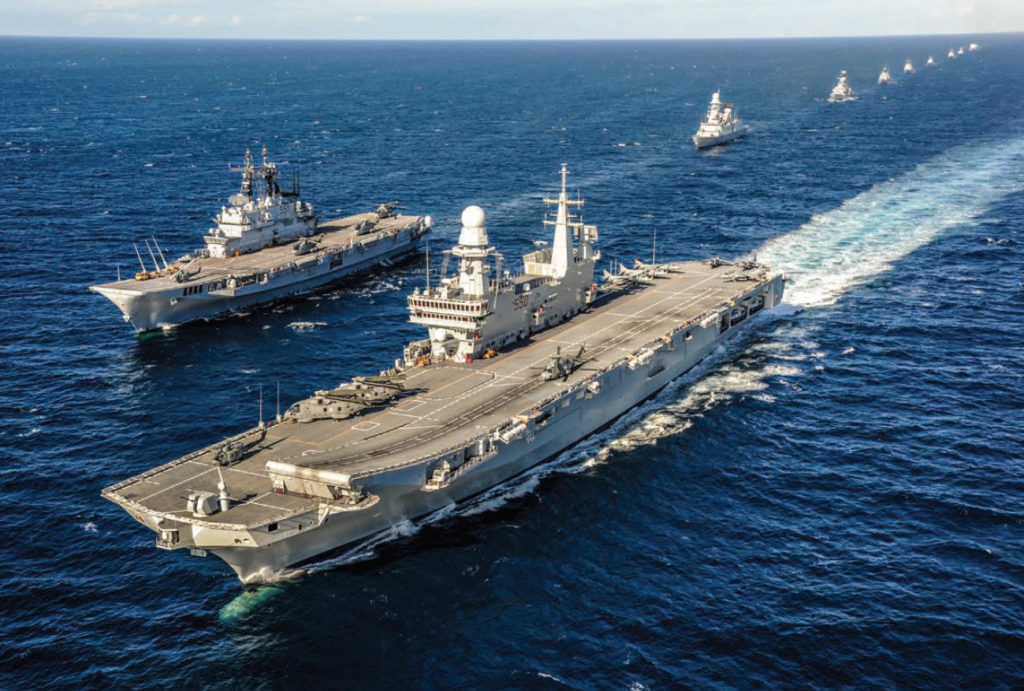
10. Italian Navy: Mediterranean Power in the Top 10 Navies of the World
The Italian Navy formed in 1946 from the Regia Marina. It rebuilt post-World War II for NATO. Moreover, the 1950s saw US aid. Expansion occurred in the 1980s for Mediterranean roles. Additionally, the 2000s carrier builds. The navy modernised for humanitarian missions. However, budget constraints limited. This led to EU partnerships. Furthermore, it focuses on regional security. Overall, it maintains influence.
Specifications include 54 warships in 2025. The fleet has 2 carriers, Cavour-class. Submarines number 8, with Todaro-class. Moreover, destroyers like Horizon-class total 4. Frigates are 10 Bergamini-class. The budget is $4 billion yearly. Additionally, tonnage is 232,046. Carriers displace 27,000 tonnes. Submarines feature AIP systems. This supports EU operations.
Operators are the Italian Republic. It deploys from La Spezia and Taranto. Moreover, bases in Sicily. The navy patrols Libya waters. Additionally, it joins Operation Sophia. No foreign operators. However, alliances with France share designs. Overall, it secures seas.
Pros include versatile carriers for air. It deploys stealth frigates effectively. Moreover, advanced submarines for stealth. Integration with EU enhances. The quality provides edge. Additionally, amphibious roles in migrations. Effectiveness in missions. Furthermore, mine countermeasures excel. This fits regional needs.
Cons involve small numbers. Budget limits expansions. Moreover, ageing vessels need replacement. Crew shortages affect. The fleet vulnerabilities to submarines exist. Additionally, short global reach. Political issues delay. However, partnerships help. Overall, it requires boost.

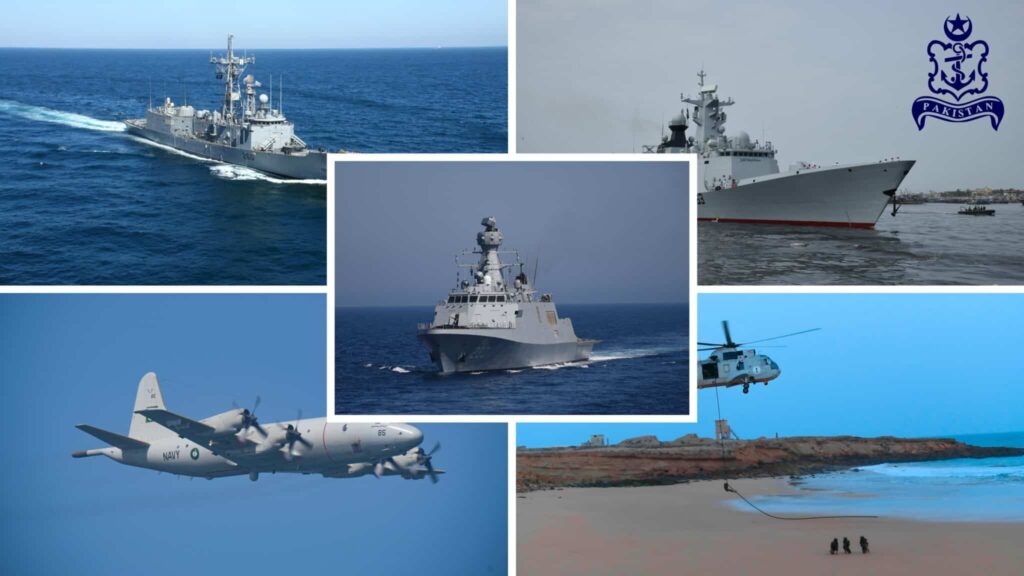
Pakistan Navy – Special Mention
The Pakistan Navy, though smaller in size compared to regional rivals, operates with a doctrine built around agility, precision, and sea denial. This strategy is tailored to its primary theater, the Arabian Sea, where geography and short engagement distances give the defender a unique advantage.
Today, Pakistan’s submarine arm remains its ace card. The Agosta-90B Khalid-class submarines, equipped with Air-Independent Propulsion (AIP), can operate silently for extended periods and strike targets with heavyweight torpedoes or Exocet SM39 anti-ship missiles. These subs can threaten high-value targets like aircraft carriers or large destroyers before they ever approach Pakistani waters. The confined North Arabian Sea further amplifies their lethality, as enemy warships have limited maneuvering space and reduced escape options.
The Navy’s modernization has also embraced indigenous missile technology. In 2018, the Harbah naval cruise missile was successfully launched from the fast-attack craft PNS Himmat, striking a target beyond the horizon. Harbah offers both anti-ship and land-attack capabilities with a range of up to 280 kilometers, surpassing older imported systems. Complementing this is the Zarb coastal defense missile, tested in 2017, which allows land-based targeting of hostile ships.
Additionally, new Type 054A/P frigates, equipped with advanced LY-80 long-range surface-to-air missiles, are expanding Pakistan’s defensive perimeter. This layered approach — combining submarines, fast-attack craft, shore-based missiles, and modern frigates — means that any adversary would face multiple, simultaneous threats.
In strategic terms, Pakistan cannot match the Indian Navy in numbers, but it does not aim to. Instead, it focuses on making the Arabian Sea a high-risk zone for hostile operations. The doctrine is simple: deny the enemy freedom of maneuver, protect maritime trade routes, and keep strategic ports like Karachi and Gwadar secure. With growing integration of drones, electronic warfare, and stealth platforms, the Pakistan Navy is positioning itself as a potent asymmetric deterrent, ensuring that any potential naval confrontation comes at an unacceptably high cost for its opponent.

Conclusion: Reflecting on the Top 10 Navies of the World
From the United States Navy to the Italian Navy, these top 10 navies of the world demonstrate diverse strategies. In 2025, carriers and submarines define power projection. Moreover, fleets like China’s show numerical growth. However, technology trumps size for others. Therefore, understanding top 10 navies of the world reveals geopolitical shifts. As tensions rise in seas, investments rise too. Additionally, alliances strengthen capabilities. The future holds unmanned vessels and hypersonics. This evolves naval warfare. Overall, these navies safeguard interests worldwide.