(By Khalid Masood)
In the evolving field of armored warfare, main battle tanks remain essential for ground forces worldwide. These vehicles combine firepower, protection, and mobility to dominate battlefields. Moreover, they adapt to modern threats like drones and anti-tank missiles. As we examine 2025, the top 10 main battle tanks showcase advanced technology and proven designs. For instance, many feature active protection systems and digital networks for better coordination. Additionally, armies prioritize tanks that balance cost and performance. However, older models still excel in reliability and availability. The keyword “top 10 main battle tanks” emphasizes those widely used by global militaries. This article explores each tank’s history, specifications, operators, pros, and cons based on recent analyses. Furthermore, it answers questions like “what are the best main battle tanks in 2025?” or “which tanks equip major armies?” Drawing from defense reports and expert sources, we provide in-depth insights. Therefore, readers can appreciate these powerful machines.
Main battle tanks typically weigh over 50 tons and carry 120mm guns. They offer all-terrain mobility and crew protection against explosives. Additionally, electronic systems enhance targeting accuracy. According to data, Russia and China lead in tank numbers, but Western designs focus on quality. Meanwhile, emerging nations adopt hybrid models for affordability. However, conflicts like Ukraine highlight vulnerabilities to new weapons. Consequently, the top 10 main battle tanks represent a mix of innovation and tradition. Armies in NATO, Asia, and the Middle East rely on them for operations. For example, special units prefer tanks with urban combat features. Overall, these vehicles shape military strategies. As technology advances, upgrades keep them relevant. Thus, this list highlights leading models in 2025.
1. M1A2 Abrams SEP v3: The American Powerhouse
The M1A2 Abrams SEP v3 evolved from the original Abrams design in the 1980s. General Dynamics developed it to meet modern combat needs. Moreover, upgrades began in the 2010s to improve electronics and armor. It entered service around 2017 with U.S. forces. Additionally, testing occurred in various environments for reliability. This variant addresses threats from advanced missiles and drones. Furthermore, it incorporates lessons from Iraq and Afghanistan wars. The U.S. Army uses it as a standard tank. Production continues at facilities in Ohio. However, exports require government approval. Overall, it represents U.S. armored superiority.
Key specifications include a weight of 73.6 short tons. The length measures 32.04 feet with the gun forward. Armament features a 120mm M256 smoothbore gun. The engine is a Honeywell AGT1500 turbine with 1,500 horsepower. Speed reaches 42 mph on roads. Range extends to 265 miles on roads. Moreover, it carries 40 rounds for the main gun. Secondary weapons include machine guns for infantry support. The crew consists of four members. Armor uses depleted uranium composites for protection. Additionally, it has NBC defense systems. This setup ensures versatility in battles.
Operators primarily include the U.S. Army with thousands in service. Australia and Poland also use variants. Egypt assembles them locally. Saudi Arabia deploys them in regional conflicts. Iraq received them for counter-terrorism. Ukraine got some for defense against Russia. Furthermore, Taiwan plans to acquire them. The tank sees action in training and deployments. However, some nations prefer lighter alternatives. Overall, it equips allied forces globally.
Pros feature advanced fire control for accurate shooting. The turbine engine provides quick acceleration. Moreover, networking allows real-time data sharing. Armor resists kinetic and chemical attacks. The APU runs electronics without the main engine. This reduces fuel use in static positions. Additionally, it excels in open terrain battles. Crew safety improves with blowout panels. The design supports upgrades easily. Therefore, it remains effective in 2025.
Cons involve high fuel consumption of up to 3 gallons per mile. The weight limits bridge crossings in some areas. Moreover, maintenance requires specialized tools. Cost per unit reaches $24 million. Logistics challenge remote operations. The turbine is noisy in stealth scenarios. Additionally, urban combat exposes vulnerabilities. Repairs take time in the field. However, upgrades mitigate some issues. Overall, it demands significant resources.
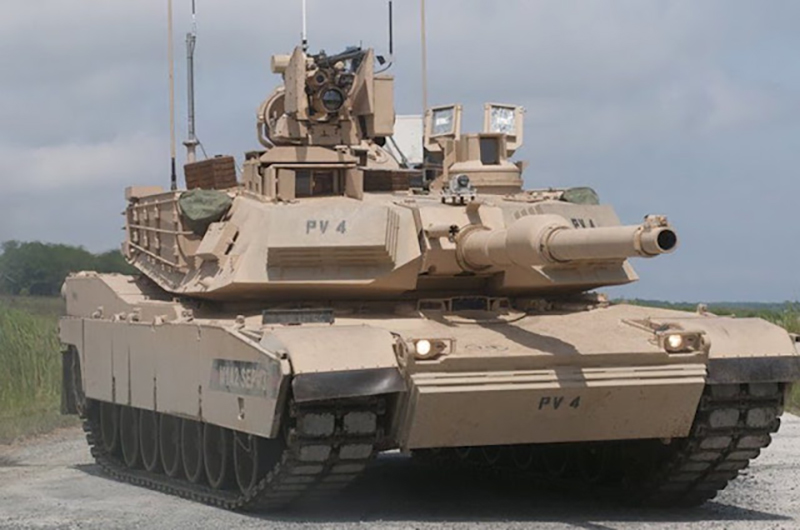

2. Leopard 2A7A1: The German Engineering Marvel
The Leopard 2A7A1 builds on the Leopard 2 series from the 1970s. Krauss-Maffei designed it for the German Army. Moreover, the A7 variant entered service in 2014. Upgrades include the Trophy active protection system. Testing concluded in 2024 for deployment in 2025. Additionally, it addresses mine and RPG threats. This model evolves from experiences in Afghanistan. The Bundeswehr uses it as a primary tank. Production focuses on modular enhancements. However, exports face restrictions. Overall, it embodies European armored innovation.
Key specifications show a weight of around 66.5 tonnes. The length is 10.97 meters with the gun forward. Armament includes a 120mm L55 smoothbore gun. The engine is an MTU MB 873 Ka-501 with 1,500 horsepower. Speed tops 70 km/h on roads. Range reaches 340 km on roads. Moreover, it holds 42 rounds for the main gun. Secondary arms are 7.62mm machine guns. The crew numbers four. Armor uses advanced composites. Additionally, it has thermal imaging. This configuration boosts combat effectiveness.
Operators include Germany with upgrades to existing fleets. Poland and Hungary deploy variants. Spain and Greece use them in NATO exercises. Canada operated them in Afghanistan. Indonesia and Qatar adopted them recently. Furthermore, Ukraine received some for defense. The tank participates in multinational drills. However, some countries opt for alternatives. Overall, it strengthens alliance capabilities.
Pros highlight exceptional mobility and speed. The fire control system engages moving targets accurately. Moreover, the Trophy APS intercepts threats. Armor provides high protection levels. Low noise aids stealth operations. Additionally, it performs well in cold climates. Crew comfort improves with ergonomics. The design allows quick repairs. Therefore, it suits diverse missions.
Cons involve high maintenance costs of €13-15 million per unit. The weight affects transport by air. Moreover, ammunition storage poses risks if hit. Logistics require trained personnel. The gun range limits in some scenarios. Additionally, urban areas expose sides. Upgrades add complexity. However, reliability remains strong. Overall, it requires substantial investment.
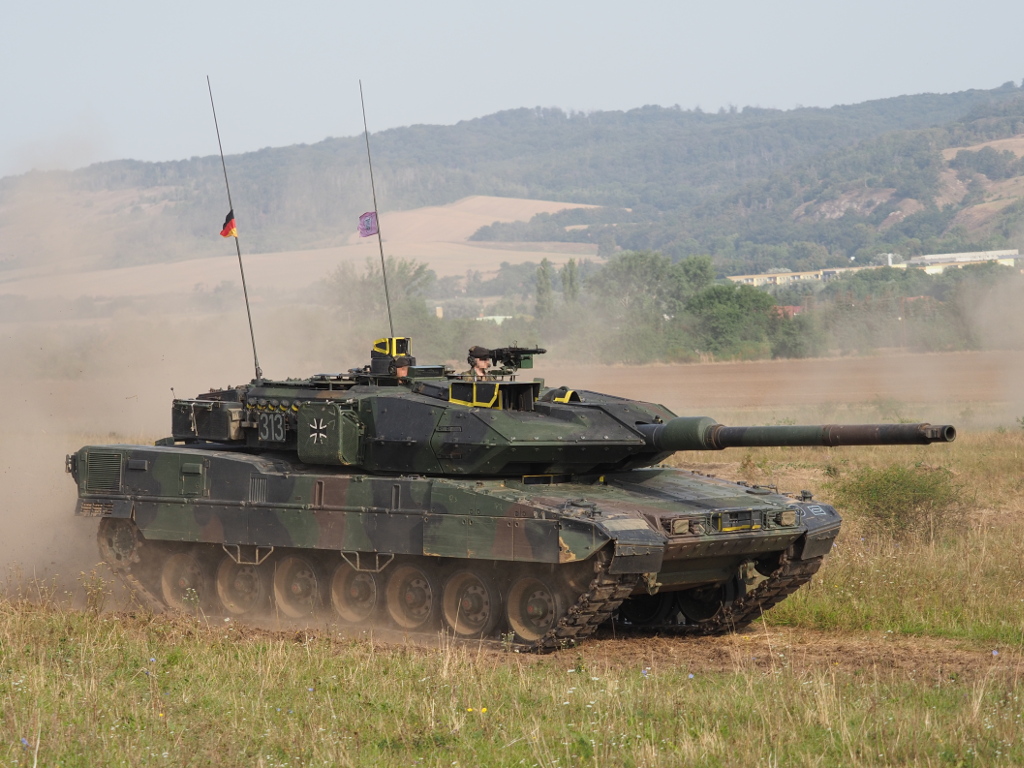

3. K2 Black Panther: The South Korean Innovator
The K2 Black Panther development started in the 1990s. Hyundai Rotem built it for the Republic of Korea Army. Moreover, it entered service in 2014. Upgrades include local powerpacks by 2020. Testing occurred in various terrains. Additionally, it addresses export needs. This tank replaces older models like the M48. The army deployed it for border security. Production resumed in 2019. However, initial issues delayed full rollout. Overall, it represents Asian technological advance.
Key specifications include a weight of 55-56 tonnes. The length is 10.8 meters overall. Armament features a 120mm CN08 smoothbore gun. The engine is an MTU MT883 Ka-501 with 1,500 horsepower. Speed reaches 70 km/h on roads. Range extends to 450 km. Moreover, it carries 40 rounds for the main gun. Secondary weapons are machine guns. The crew is three. Armor uses composites and ERA. Additionally, it has hydropneumatic suspension. This setup enhances maneuverability.
Operators are the Republic of Korea Army with 260 units. Poland acquired 133 for its forces. Saudi Arabia considered exports. Egypt showed interest. Furthermore, Peru agreed to 100 units. Romania tested it in 2024. The tank sees use in exercises. However, some nations await localization. Overall, it expands regional influence.
Pros feature high-tech fire control for moving targets. The autoloader reduces crew size. Moreover, APS defends against missiles. Mobility suits mountainous areas. Low profile aids concealment. Additionally, it fords deep water. Digital systems integrate with drones. The design supports upgrades. Therefore, it excels in modern warfare.
Cons involve reliance on imported parts initially. The cost limits mass production. Moreover, transmission issues occurred early. Weight affects some bridges. Logistics challenge remote areas. Additionally, export deals face delays. Maintenance requires specialized skills. However, domestic production improves. Overall, it demands ongoing development.

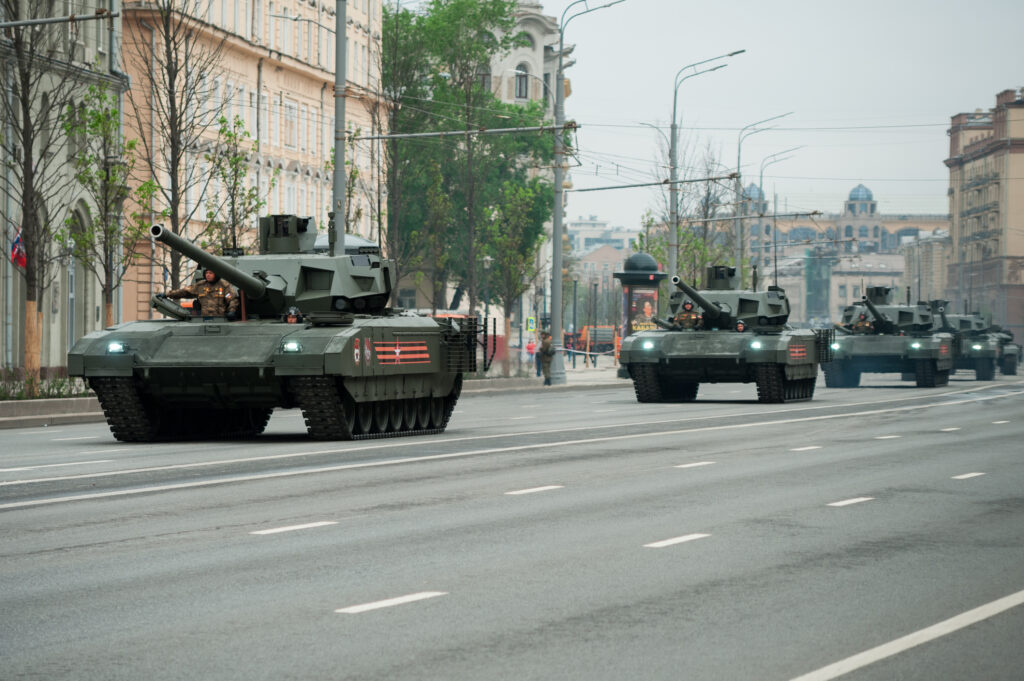
4. T-14 Armata: The Russian Next-Gen Tank
The T-14 Armata development began after the T-95 cancellation in 2010. Uralvagonzavod designed it for the Russian Army. Moreover, it debuted in 2015 at the Victory Day Parade. Trials started in 2020. Additionally, production faced delays due to sanctions. This tank aims to replace older T-72 models. The army tested it in Syria. Serial production announced in 2021. However, only small batches exist. Overall, it symbolizes Russian innovation.
Key specifications show a weight of 55 tonnes. The length is 10.7 meters. Armament includes a 125mm 2A82-1M smoothbore gun. The engine is a 12N360 diesel with 1,500 horsepower. Speed reaches 75-80 km/h. Range is at least 500 km. Moreover, it holds 45 rounds. Secondary arms are machine guns. The crew is three. Armor uses steel and ERA. Additionally, it has an unmanned turret. This layout boosts safety.
Operators are the Russian Armed Forces with limited units. China and India showed interest. Egypt considered purchases. Belarus may adopt it. Furthermore, Vietnam explored options. The tank appears in parades. However, no widespread deployment. Overall, it focuses on domestic use.
Pros highlight unmanned turret for crew protection. The APS intercepts projectiles. Moreover, sensors provide 360-degree view. Mobility suits rough terrain. Digital networks enhance coordination. Additionally, it fires guided missiles. Stealth features reduce detection. The design allows upgrades. Therefore, it offers future-proof capabilities.
Cons involve high cost of $3.7-7.1 million per unit. Production delays limit numbers. Moreover, engine issues occurred. Sanctions affect parts supply. Logistics challenge maintenance. Additionally, combat testing is limited. Vulnerabilities to top attacks exist. However, potential remains high. Overall, it faces implementation hurdles.

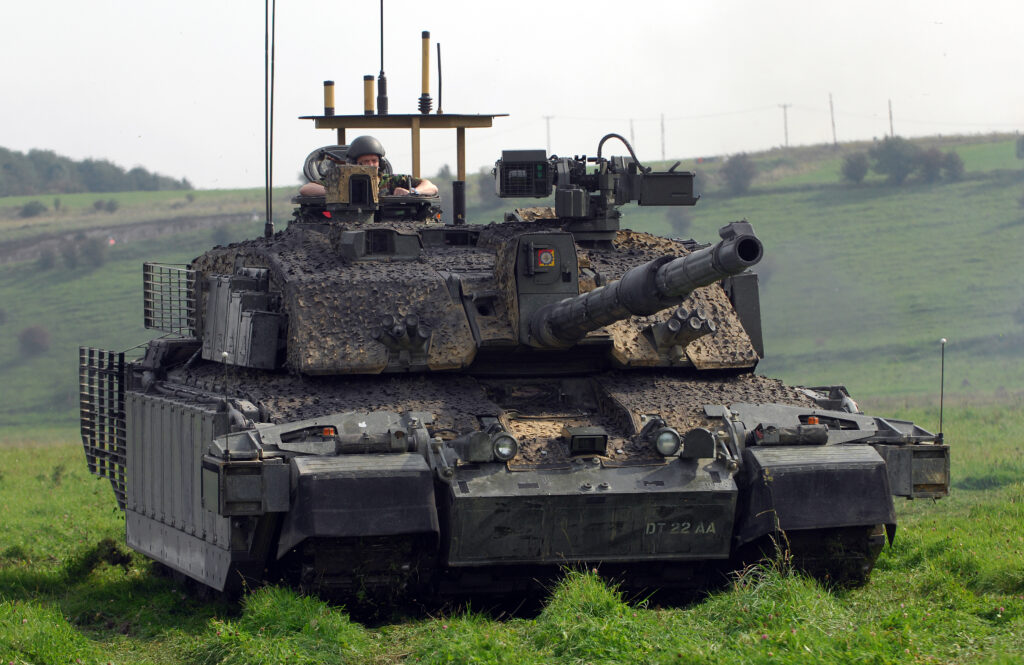
5. Challenger 2: The British Stalwart
The Challenger 2 development started in 1986 by Vickers. It entered service in 1998 with the British Army. Moreover, it replaced the Challenger 1. Upgrades include armor enhancements. Additionally, it saw action in Iraq and Kosovo. This tank focuses on protection and accuracy. The army plans Challenger 3 replacement from 2027. Production ended in 2002. However, exports to Oman succeeded. Overall, it upholds UK armored tradition.
Key specifications include a weight of 64 tons standard. The length is 13.5 meters with gun forward. Armament features a 120mm L30A1 rifled gun. The engine is a Perkins CV12-6A with 1,200 horsepower. Speed reaches 59 km/h on roads. Range extends to 550 km on roads. Moreover, it carries 47 rounds. Secondary weapons are machine guns. The crew is four. Armor uses Chobham composites. Additionally, it has hydropneumatic suspension. This configuration ensures durability.
Operators are the British Army with 219 units. Oman has 38 in service. Ukraine received 14 for defense. Jordan uses them. Furthermore, other nations considered purchases. The tank participates in NATO missions. However, some are in storage. Overall, it supports allied operations.
Pros feature exceptional armor against HEAT rounds. The rifled gun fires HESH effectively. Moreover, fire control improves long-range hits. Mobility handles diverse terrains. Crew protection is high with NBC systems. Additionally, it has low thermal signature. The design allows urban kits. Therefore, it suits modern conflicts.
Cons involve slower speed compared to peers. The weight limits air transport. Moreover, rifled gun requires specific ammo. Cost per unit is high. Logistics need heavy equipment. Additionally, losses in Ukraine show drone vulnerabilities. Maintenance is complex. However, upgrades address issues. Overall, it requires careful deployment.

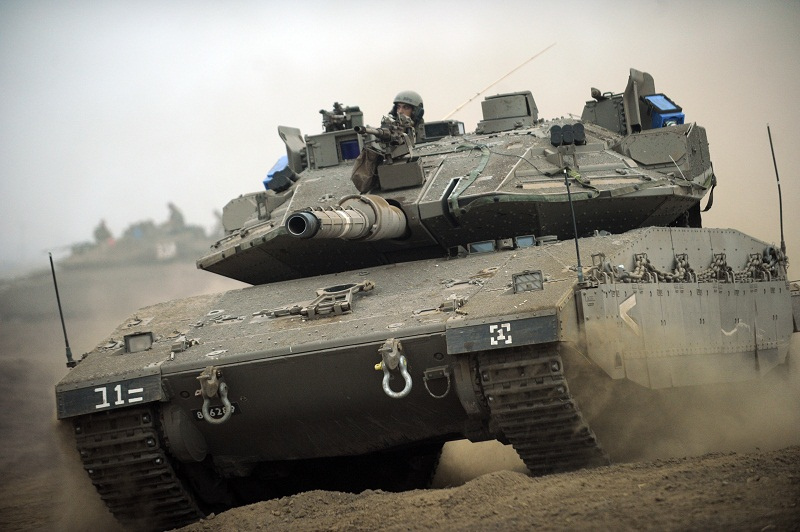
6. Merkava Mk 4: The Israeli Defender
The Merkava Mk 4 development began in 1999. It entered service in 2004 with the IDF. Moreover, it builds on earlier Merkava models. Upgrades include the Trophy APS. Additionally, it saw use in Lebanon and Gaza wars. This tank emphasizes crew survival and urban combat. The IDF deploys it in border security. Production continues for domestic needs. However, exports are limited. Overall, it reflects Israeli engineering focus.
Key specifications show a weight of 65 tonnes. The length is 9.04 meters including gun. Armament includes a 120mm MG251-LR smoothbore gun. The engine is an MTU 12V883 with 1,501 horsepower. Speed reaches 64 km/h on roads. Range is 500 km. Moreover, it carries 48 rounds. Secondary arms are machine guns and mortar. The crew is four. Armor is modular composites. Additionally, it has front engine placement. This design protects the crew.
Operators are the Israel Defense Forces exclusively. Philippines uses bridge variants. Cyprus discussed purchases. Furthermore, no other exports confirmed. The tank operates in Middle East conflicts. However, some are for reserves. Overall, it serves national defense.
Pros highlight front engine for extra protection. The Trophy APS defeats missiles. Moreover, BMS integrates with UAVs. Firepower includes ATGM launches. Crew comfort features air conditioning. Additionally, it handles urban environments well. The modular armor allows quick fixes. Therefore, it excels in asymmetric warfare.
Cons involve heavy weight for mobility issues. The cost is $3.5-10 million per unit. Moreover, rear armor is thinner. Logistics require support vehicles. Urban combat exposes vulnerabilities. Additionally, conflicts show IED risks. Maintenance is specialized. However, survivability is high. Overall, it demands strategic use.

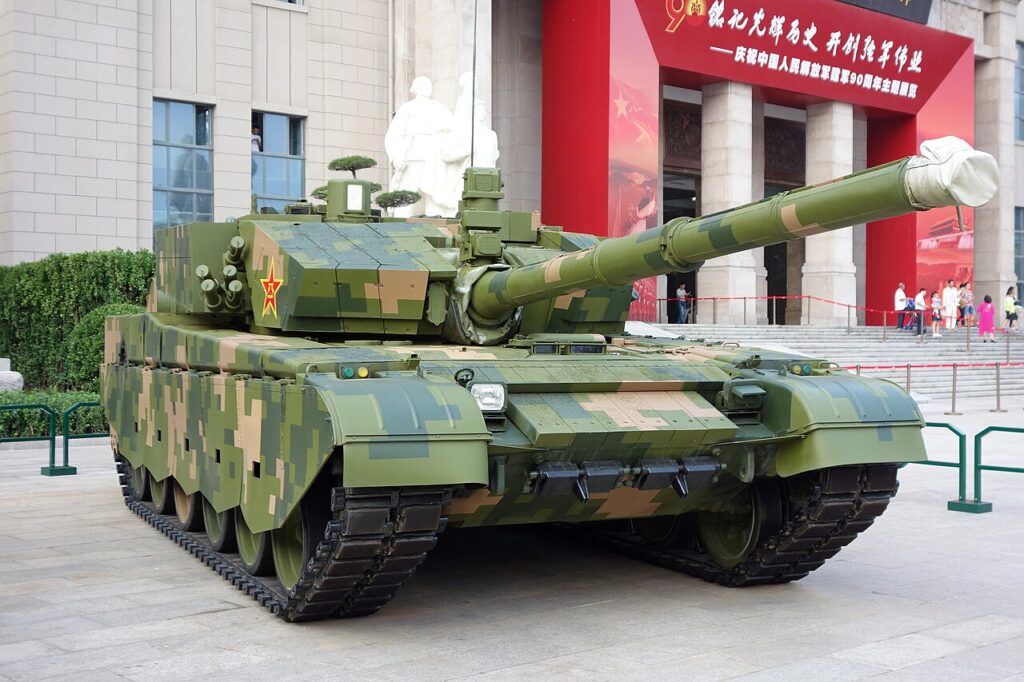
7. Type 99A: The Chinese Contender
The Type 99A development started in the 2000s. It entered service in 2011 with the PLA. Moreover, it improved on the base Type 99. Upgrades include ERA and fire control. Additionally, it appeared in parades and exercises. This tank boosts China’s armored strength. The army deploys it in border regions. Production focuses on quality. However, numbers remain limited. Overall, it marks Chinese progress.
Key specifications include a weight of 55 tonnes. The length is 11 meters gun forward. Armament features a 125mm ZPT-98 smoothbore gun. The engine is a 150HB diesel with 1,500 horsepower. Speed reaches 76 km/h on roads. Range is 600-650 km. Moreover, it carries 42 rounds. Secondary weapons are machine guns. The crew is three. Armor uses composites and ERA. Additionally, it has laser defense systems. This setup enhances lethality.
Operators are the People’s Liberation Army Ground Force only. No exports reported. Furthermore, it participates in SCO drills. The tank equips elite units. However, deployment is selective. Overall, it supports national security.
Pros feature hunter-killer capabilities for targets. The autoloader speeds firing. Moreover, APS counters threats. Mobility suits vast terrains. Digital systems aid coordination. Additionally, it has millimeter wave radar. The design allows all-weather operations. Therefore, it fits modern doctrines.
Cons involve high cost limiting quantities. The laser system struggles in bad weather. Moreover, export restrictions apply. Logistics need improvement. Vulnerability to advanced penetrators exists. Additionally, crew training is intensive. Maintenance requires parts. However, upgrades continue. Overall, it has growth potential.

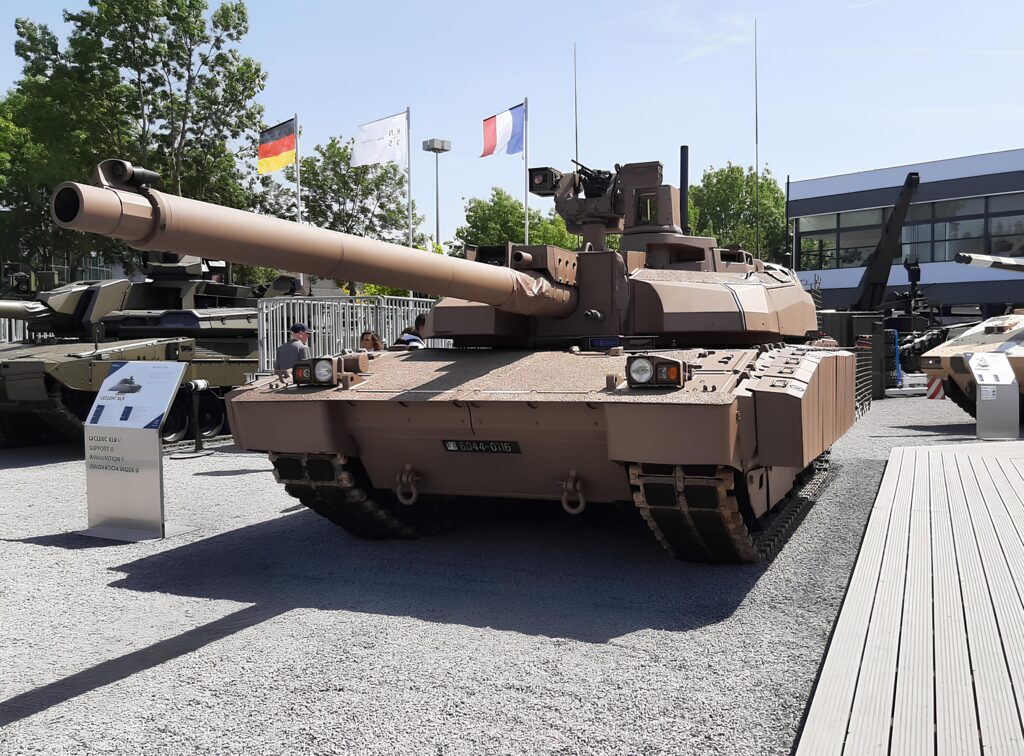
8. Leclerc XLR: The French Versatile Tank
The Leclerc development began in the 1980s. It entered service in 1992 with the French Army. Moreover, the XLR upgrade started in 2023. Upgrades include new electronics and armor. Additionally, it integrates with Scorpion systems. This variant modernizes 200 tanks by 2029. The army uses it in deployments. Production is by KNDS France. However, exports to UAE succeeded. Overall, it embodies French mobility focus.
Key specifications show a weight of 56.3-57.6 tonnes. The length is 9.87 meters. Armament includes a 120mm CN120-26/52 gun. The engine is a V8X SACM with 1,500 horsepower. Speed reaches 71 km/h on roads. Range is 550 km. Moreover, it carries 40 rounds. Secondary arms are machine guns. The crew is three. Armor is composites with add-ons. Additionally, it has autoloader. This configuration ensures speed.
Operators are the French Army with upgrades. UAE has 388 units. Jordan uses them. Furthermore, no other confirmed. The tank deploys in Africa. However, some are in storage. Overall, it aids international missions.
Pros feature high speed and agility. The fire control handles multi-mode rounds. Moreover, BMS enhances networking. Protection improves with IED jammers. Crew reduction saves manpower. Additionally, it has low profile. The design supports urban kits. Therefore, it suits rapid response.
Cons involve high cost of €16 million. The weight affects some operations. Moreover, upgrades delay timelines. Logistics require support. Vulnerability to mines exists. Additionally, export deals are limited. Maintenance is technical. However, versatility is strong. Overall, it needs sustained funding.

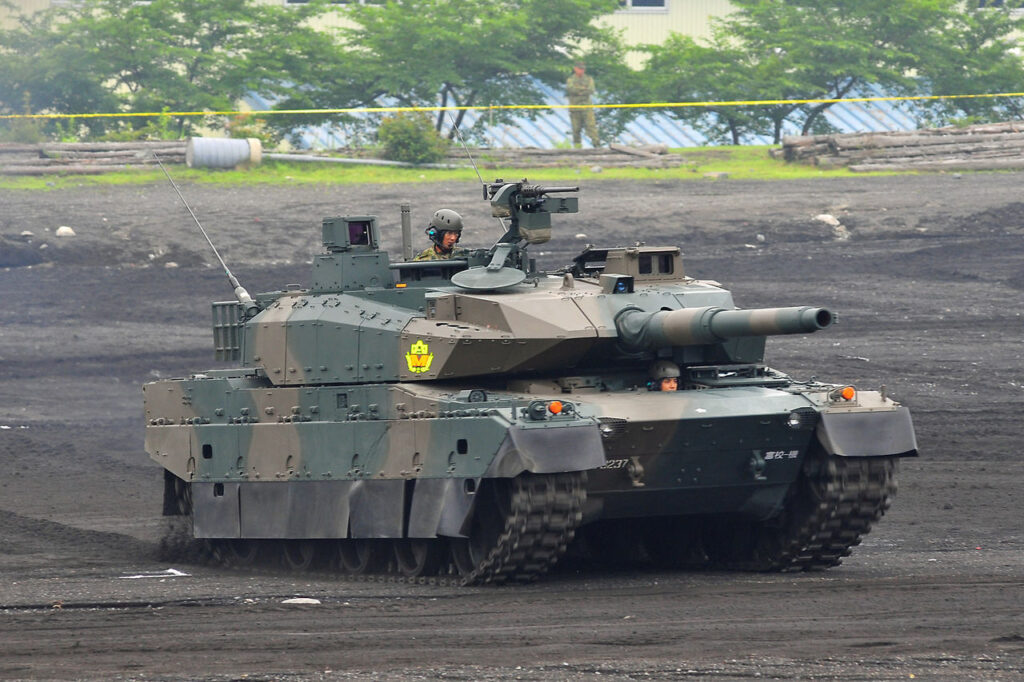
9. Type 10: The Japanese Compact Warrior
The Type 10 development began in the 1990s. Mitsubishi built it for the JGSDF. Moreover, it entered service in 2012. Upgrades include C4I systems. Additionally, it replaces older Type 74. This tank addresses Japan’s terrain challenges. The force deploys it for defense. Production reached 129 by 2024. However, budget limits numbers. Overall, it highlights Japanese precision.
Key specifications include a weight of 40-48 tonnes. The length is 9.485 meters. Armament features a 120mm smoothbore gun. The engine is a V8 diesel with 1,200 horsepower. Speed reaches 70 km/h. Range is 500 km. Moreover, it carries 36 rounds. Secondary arms are machine guns. The crew is three. Armor is modular ceramics. Additionally, it has hydropneumatic suspension. This setup boosts flexibility.
Operators are the Japan Ground Self-Defense Force with 129 units. No exports due to laws. Furthermore, it trains in exercises. The tank suits island defense. However, production is slow. Overall, it serves homeland protection.
Pros feature lightweight for bridge crossings. The C4I integrates data sharing. Moreover, modular armor adapts to threats. Mobility fits narrow roads. Stealth reduces signatures. Additionally, it has automatic loader. The design allows quick transport. Therefore, it matches Japan’s needs.
Cons involve high cost of $11.3 million. The armor protects less in full load. Moreover, export bans limit sales. Logistics need airlift. Vulnerability to heavy fire exists. Additionally, crew training is rigorous. Maintenance requires expertise. However, efficiency is high. Overall, it has niche advantages.

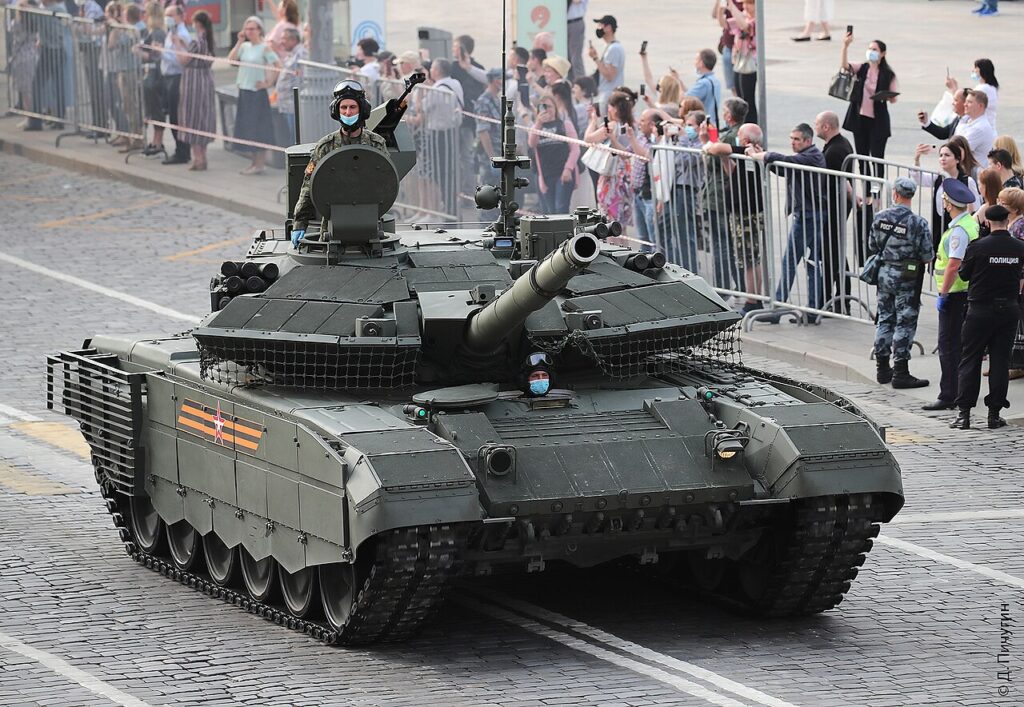
10. T-90M: The Russian Reliable Upgrade
The T-90M development started in the 2010s. Uralvagonzavod upgraded it from the T-90. Moreover, it appeared in 2017. Upgrades include Relikt ERA. Additionally, it entered service in 2020. This variant responds to Ukraine losses. The army deploys it in conflicts. Production surged to 300 in 2024. However, sanctions affect output. Overall, it sustains Russian forces.
Key specifications show a weight of 48 tonnes. The length is 9.63 meters. Armament includes a 125mm 2A46M-5 gun. The engine is a V-92S2F with 1,130 horsepower. Speed reaches 60 km/h. Range is 550 km. Moreover, it carries 43 rounds. Secondary arms are machine guns. The crew is three. Armor uses Relikt ERA. Additionally, it has Kalina fire control. This enhances combat.
Operators are the Russian Army with over 200 units. Egypt plans 500. Kuwait considered 146. Ukraine captured some. Furthermore, it sees use in Syria. The tank equips guards divisions. However, losses reach 134. Overall, it bolsters frontline.
Pros feature improved ERA against tandems. The fire control aids targeting. Moreover, engine boosts mobility. APS potential exists. Cost is lower than T-14. Additionally, it shares parts with T-72. The design allows quick upgrades. Therefore, it fits mass armies.
Cons involve turret spinning issues. Losses to Javelins are high. Moreover, production faces sanctions. Logistics strain supply. Vulnerability to drones persists. Additionally, electronics are poor in some. Maintenance is frequent. However, affordability helps. Overall, it has battlefield challenges.

Conclusion: The Future of Top 10 Main Battle Tanks
From the M1A2 Abrams to the T-90M, these top 10 main battle tanks demonstrate armored evolution. In 2025, active protection and networks define success. Moreover, tanks like the Leopard 2A7A1 lead in innovation. However, classics maintain roles. Therefore, understanding top 10 main battle tanks reveals military trends.